Marine biology, the study of life in the ocean, opens the door to an awe-inspiring world teeming with diversity, mystery, and wonder. Covering more than 70% of Earth’s surface, the ocean is a vast ecosystem, home to creatures that range from microscopic plankton to enormous whales. This intricate web of life not only sustains marine ecosystems but also profoundly impacts terrestrial ecosystems, climate regulation, and human life.
This article dives deep into the enchanting realm of marine biology, uncovering its significance, groundbreaking discoveries, and why it continues to captivate scientists and nature enthusiasts alike.
The Ocean: Earth’s Blue Heart
The ocean is more than just a body of water; it is the lifeblood of our planet. Key facts about the ocean’s role include:
- Climate Regulation: Oceans absorb around 30% of atmospheric carbon dioxide and distribute heat globally, mitigating extreme climate changes.
- Oxygen Production: Marine plants like phytoplankton contribute over 50% of the oxygen we breathe.
- Biodiversity: Oceans house nearly 230,000 known species, with millions yet to be discovered.
Understanding marine biology helps us appreciate the ocean’s critical functions and the urgency of preserving its health.

Key Areas of Marine Biology
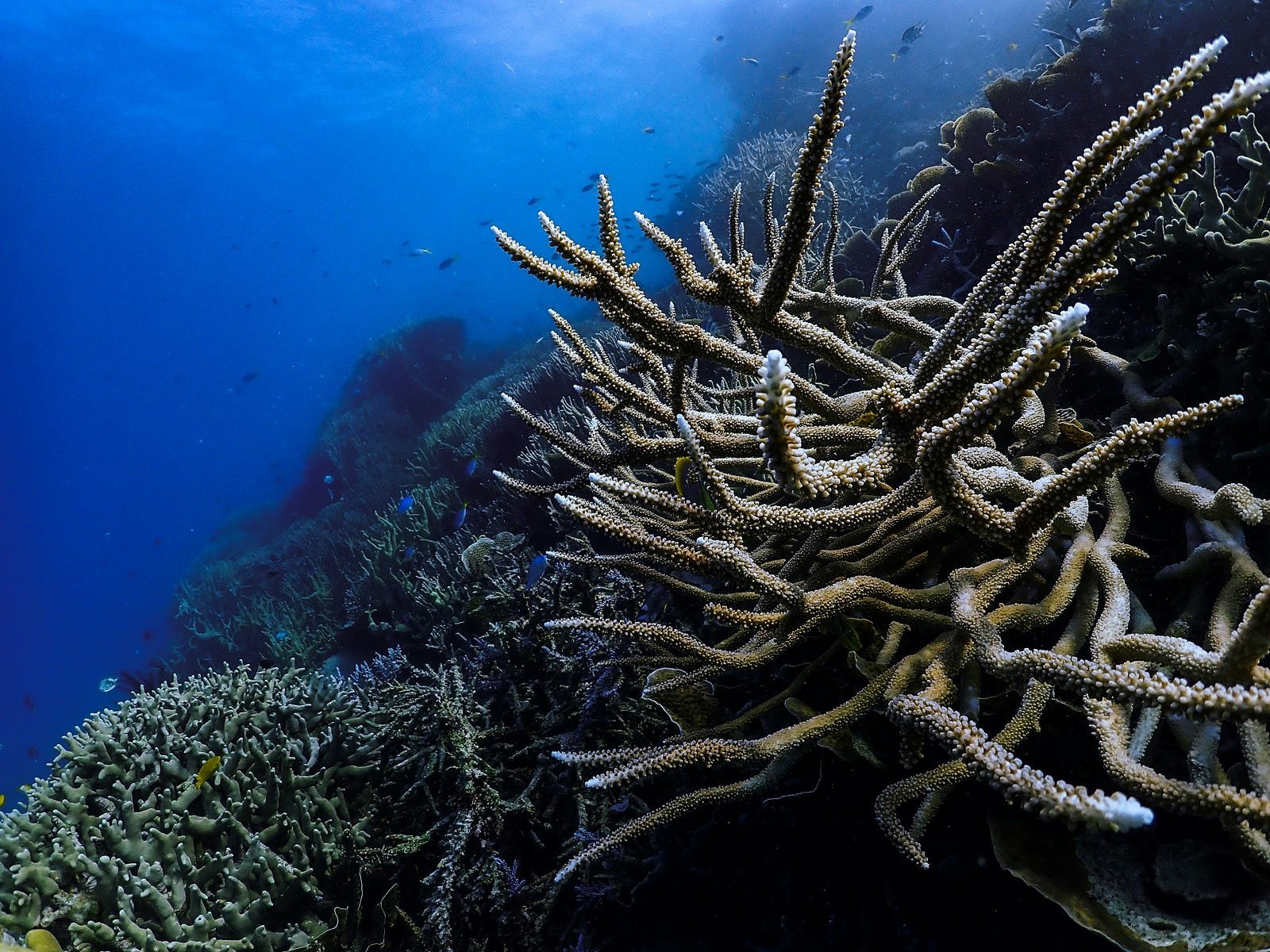
1. Coral Reefs: The Rainforests of the Sea
Coral reefs are among the most diverse marine ecosystems, supporting over 25% of marine species. Their significance includes:
- Biodiversity Hotspots: Home to colorful fish, crustaceans, mollusks, and other marine life.
- Protection Against Erosion: Coral reefs act as natural barriers, protecting coastlines from waves and storms.
- Medicinal Potential: Compounds found in reef organisms are being studied for cancer treatments, antibiotics, and more.
The decline of coral reefs due to climate change, pollution, and overfishing underscores the importance of marine biology in conservation efforts.
2. Deep-Sea Ecosystems: The Final Frontier
The deep sea is one of the least explored areas on Earth. At depths exceeding 6,000 meters, life thrives under extreme pressure, near-freezing temperatures, and complete darkness. Fascinating discoveries include:
- Bioluminescent Species: Many deep-sea creatures, such as anglerfish, produce light to attract prey or mates.
- Hydrothermal Vents: These underwater hot springs support unique ecosystems fueled by chemosynthesis instead of photosynthesis.
- Gigantism: Species like giant squids demonstrate adaptations unique to the deep ocean.
Exploring these ecosystems expands our understanding of life’s adaptability.
3. Marine Mammals: The Ocean’s Charismatic Creatures
Marine mammals such as dolphins, whales, seals, and manatees are beloved icons of the ocean. They play critical roles in marine ecosystems, including:
- Ecosystem Balance: Whales regulate fish populations and contribute to nutrient cycling.
- Social Complexity: Dolphins exhibit advanced communication, problem-solving, and social behaviors.
- Conservation Challenges: Many marine mammals face threats from habitat destruction, ship collisions, and entanglement in fishing gear.
The Tools of Marine Biology
Marine biologists use cutting-edge technology to explore and study the ocean. Key tools include:
- Remote Sensing: Satellites monitor ocean temperatures, currents, and chlorophyll levels.
- ROVs and AUVs: Remotely operated and autonomous underwater vehicles enable deep-sea exploration.
- Acoustic Tagging: Tags track marine animals’ movements, behaviors, and habitats.
- Genomics: DNA analysis reveals genetic diversity and relationships among marine species.
Advances in technology continually expand the boundaries of marine research.
Why Marine Biology Matters
Marine biology impacts various aspects of life on Earth, including:
1. Sustaining Fisheries and Food Security
Marine life provides a vital food source for billions of people. Marine biology informs sustainable fishing practices, protecting species from overfishing and ensuring long-term availability.
2. Medical Breakthroughs
Marine organisms inspire numerous medical advancements. Examples include:
- Cone Snail Venom: Studied for painkillers.
- Sea Sponges: Source of anticancer and antiviral compounds.
- Horseshoe Crab Blood: Vital for testing vaccine safety.
3. Climate Change Mitigation
Understanding marine ecosystems helps combat climate change. For example:
- Mangroves and seagrass beds sequester carbon, mitigating greenhouse gas effects.
- Coral reefs protect coastal communities from rising sea levels.
4. Biodiversity and Ecological Balance
Healthy oceans support biodiversity and provide ecosystem services such as nutrient cycling and oxygen production. Marine biology is essential for preserving these benefits.
Challenges Facing Marine Biology
Despite its importance, marine biology faces numerous challenges:
- Climate Change: Rising ocean temperatures and acidification threaten marine life.
- Pollution: Plastic waste, oil spills, and chemical runoff devastate marine ecosystems.
- Overfishing: Unsustainable fishing practices disrupt food chains and deplete stocks.
- Habitat Destruction: Coastal development and dredging damage critical habitats like mangroves and seagrasses.
Promising Initiatives in Marine Conservation
Marine biologists and conservationists are spearheading initiatives to protect ocean health, including:
- Marine Protected Areas (MPAs): Designated zones where marine life is protected from human activities.
- Sustainable Fisheries: Policies and technologies to reduce bycatch and overfishing.
- Coral Restoration: Techniques like coral gardening and micro-fragmentation to restore reefs.
- Public Awareness Campaigns: Efforts to reduce plastic use and promote ocean conservation.
How You Can Contribute
Even individuals without a marine biology background can help protect the ocean. Tips include:
- Reduce Plastic Use: Opt for reusable items and avoid single-use plastics.
- Support Sustainable Seafood: Choose seafood certified by organizations like the Marine Stewardship Council (MSC).
- Participate in Cleanups: Join local beach or river cleanups to reduce pollution.
- Educate Others: Share knowledge about marine conservation with friends and family.
Fascinating Marine Biology Facts
- The Blue Whale: The largest animal ever, reaching lengths of over 100 feet and weighing up to 200 tons.
- Octopus Intelligence: Octopuses are capable of problem-solving, tool use, and even escaping enclosures.
- Sea Turtles: Some species can live over 100 years and navigate back to their birthplace to lay eggs.
- Phytoplankton: These microscopic organisms are responsible for producing at least 50% of Earth’s oxygen.
Careers in Marine Biology
Marine biology offers diverse career paths, including:
- Research Scientist: Study marine organisms and ecosystems.
- Conservationist: Develop and implement strategies to protect marine life.
- Aquarist: Care for marine life in aquariums and rehabilitation centers.
- Environmental Consultant: Advise on policies affecting marine environments.
The Future of Marine Biology
Emerging technologies and interdisciplinary collaborations promise a bright future for marine biology. Key trends include:
- Artificial Intelligence: AI analyzes vast data sets, improving conservation strategies.
- Citizen Science: Public participation in projects like species identification and water quality monitoring.
- International Cooperation: Countries working together to combat global issues like overfishing and pollution.
The fascinating world of marine biology is a testament to the beauty, complexity, and importance of Earth’s oceans. As we continue to explore and understand the mysteries beneath the waves, it becomes clear that protecting marine life is essential for the well-being of the planet.
Through science, conservation, and individual efforts, we can ensure that future generations inherit a thriving ocean teeming with life. Whether you’re a scientist, student, or ocean enthusiast, the wonders of marine biology invite us all to dive in and make a difference.