In a world facing the urgent challenge of climate change, sustainable technologies are at the forefront of our efforts to transition to a greener future. Among the most impactful innovations are solar power, wind energy, and electric vehicles (EVs). These technologies not only help reduce greenhouse gas emissions but also provide long-term solutions to the planet’s energy and transportation needs.
This article delves into these innovative sustainable technologies, exploring their current impact, future potential, and how they are reshaping industries and daily life. Let’s take a closer look at how solar power, wind energy, and electric vehicles are driving the global shift toward sustainability.
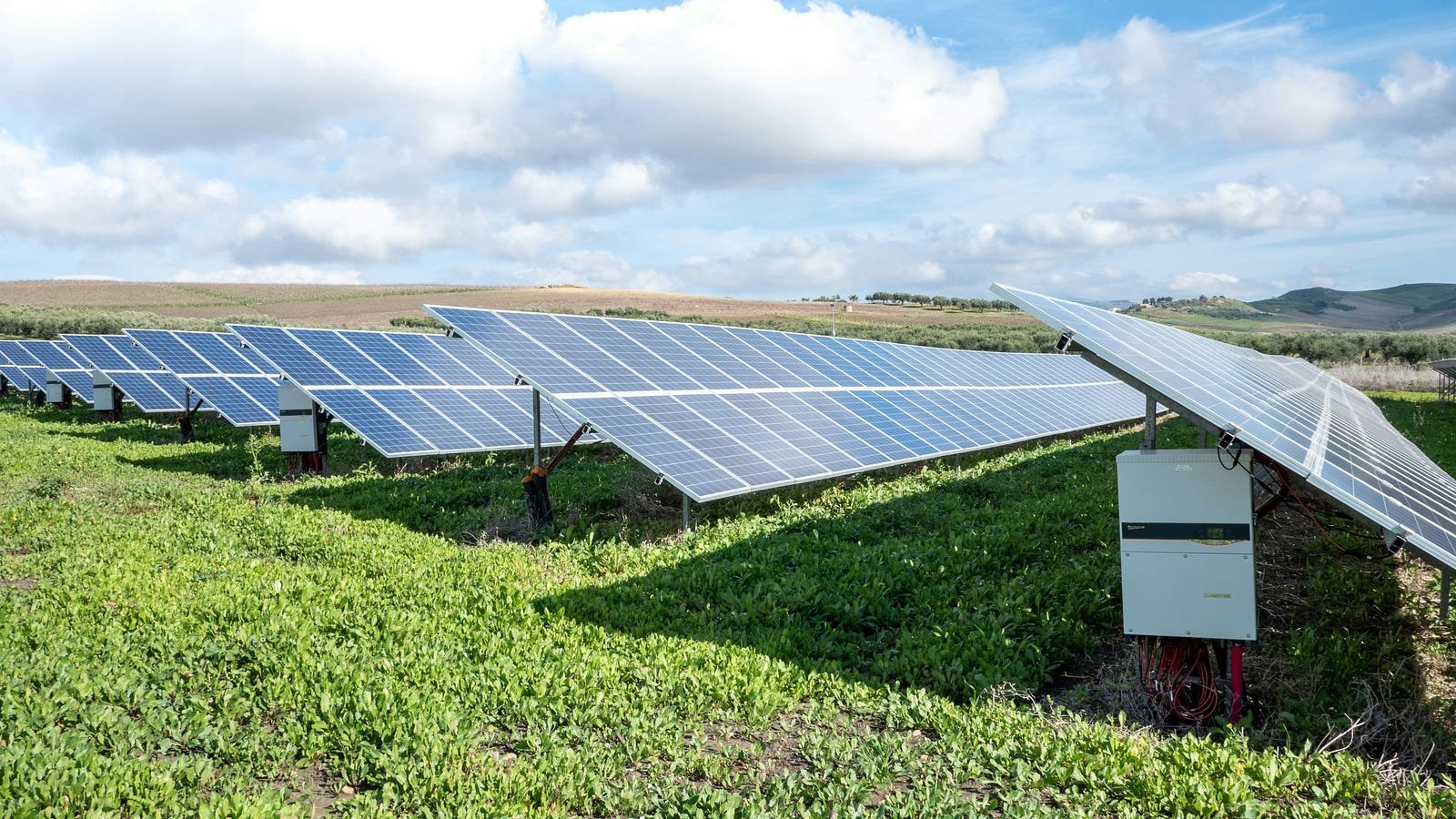

1. Solar Power: Harnessing the Sun’s Energy
Solar power is one of the most abundant and accessible forms of renewable energy. By capturing sunlight through photovoltaic (PV) panels or concentrated solar power (CSP) systems, we can generate electricity without emitting harmful pollutants.
How Solar Power Works
Photovoltaic Panels (PV): PV panels are the most common form of solar technology. These panels convert sunlight directly into electricity using semiconductors, typically made of silicon, that create an electric current when exposed to sunlight.
Concentrated Solar Power (CSP): CSP uses mirrors or lenses to focus sunlight onto a small area, which then generates heat that is used to produce electricity through traditional turbines.
Benefits of Solar Power
Clean and Renewable: Solar energy is abundant, free, and non-polluting. Unlike fossil fuels, it doesn’t release harmful emissions into the atmosphere.
Energy Independence: Solar power allows individuals and businesses to generate their own energy, reducing dependence on external energy providers.
Cost Reduction: Solar installations can significantly lower electricity bills. In many regions, government incentives and subsidies help make solar power even more affordable.
Current and Future Outlook
Solar energy has already made significant strides, and costs continue to drop, making it more accessible. In fact, the price of solar panels has decreased by over 80% in the past decade, making solar power one of the most cost-effective forms of energy available. With advancements in energy storage technologies, like batteries, solar power will become even more reliable and efficient.
2. Wind Energy: Powering the Future with Wind Turbines
Wind energy is another cornerstone of sustainable energy solutions. Using wind turbines to capture the kinetic energy from wind, we can generate electricity on both large and small scales. Wind power offers a clean and renewable alternative to fossil fuels, making it a key player in the global push for sustainability.
How Wind Energy Works
Wind turbines consist of large blades mounted on a tall tower that spin when wind passes over them. This motion turns a generator that produces electricity. Wind farms, which can be located onshore or offshore, are equipped with multiple turbines working together to generate large amounts of power.
Benefits of Wind Energy
Renewable and Sustainable: Wind is inexhaustible and doesn’t pollute the air or water.
Large-Scale Power Generation: Wind farms can generate significant amounts of electricity, sometimes providing power to entire communities or regions.
Job Creation: The wind industry has created thousands of jobs in manufacturing, installation, and maintenance of turbines, contributing to economic growth.
Challenges and Innovations
While wind energy has made substantial progress, it does face some challenges:
Intermittency: Wind energy generation is dependent on weather conditions, which can fluctuate.
Storage: Like solar, wind energy requires storage solutions to ensure a stable power supply.
To address these issues, new technologies like smart grids and advanced energy storage systems are being developed to improve the reliability and efficiency of wind energy.
3. Electric Vehicles (EVs): Revolutionizing Transportation
Electric vehicles (EVs) represent a pivotal shift in how we think about transportation. Unlike traditional gasoline-powered vehicles, EVs run on electric power stored in batteries. With rising concerns about air pollution and carbon emissions from the transportation sector, EVs offer a cleaner, more sustainable alternative.
How Electric Vehicles Work
EVs are powered by batteries, typically lithium-ion, which are charged through standard electrical outlets or dedicated EV charging stations. These vehicles use electric motors instead of internal combustion engines, eliminating the need for gasoline or diesel fuel.
Benefits of Electric Vehicles
Zero Emissions: EVs produce no tailpipe emissions, making them a major contributor to improving air quality and reducing greenhouse gases.
Lower Operating Costs: EVs are generally cheaper to maintain than traditional vehicles because they have fewer moving parts and do not require regular oil changes.
Energy Efficiency: EVs are more efficient than internal combustion engines, converting a higher percentage of energy from the battery into motion.
Challenges and Innovations
Range Anxiety: One of the primary concerns for EV owners is range anxiety, or the fear that their vehicle will run out of charge before reaching a charging station. However, advancements in battery technology are steadily increasing the range of EVs.
Charging Infrastructure: While the number of charging stations is increasing, a global charging infrastructure network is still being developed to meet the growing demand for electric vehicles.
Despite these challenges, EV sales have surged in recent years. With major automakers like Tesla, Nissan, and BMW leading the way, more consumers are opting for electric vehicles. Additionally, government incentives and tax credits are making EVs more affordable and encouraging their adoption.
The Synergy Between Solar Power, Wind Energy, and Electric Vehicles
The intersection of solar power, wind energy, and electric vehicles offers a powerful, sustainable future. When combined, these technologies can create a fully integrated green energy ecosystem:
Solar-Powered EV Charging: Solar panels can be used to generate electricity for EV charging stations, reducing the carbon footprint of electric vehicles even further.
Wind Energy and EVs: Wind energy can be used to power EV charging stations or even entire fleets of electric vehicles, further reducing reliance on fossil fuels.
Energy Storage: Advanced storage systems can be developed to store excess energy from both solar and wind, ensuring a reliable power supply for EVs even when weather conditions aren’t ideal.
Together, these technologies can help create a circular economy, where renewable energy powers sustainable transportation, and both contribute to a cleaner, more resilient energy grid.
A Sustainable Future Powered by Innovation
Solar power, wind energy, and electric vehicles are reshaping the way we produce, consume, and transport energy. By continuing to innovate and invest in these technologies, we can create a sustainable future that reduces our reliance on fossil fuels, lowers greenhouse gas emissions, and fosters environmental responsibility.
With governments, businesses, and individuals all playing their part, the transition to renewable energy and sustainable transportation is not just possible — it’s already happening.